API
Quick Definition
A set of rules that allows one software application to interact with another, enabling integration and functionality.
In-Depth Explanation
Historical Context
The concept of APIs has been around since the early days of computing, but it gained significant traction with the rise of web applications in the late 1990s and early 2000s. Initially, APIs were primarily used for software libraries, but the advent of web APIs revolutionized how applications could interact over the internet.Importance in AI
In the AI field, APIs play a crucial role in enabling machine learning models and AI services to be integrated into various applications. They allow developers to leverage complex algorithms and data processing capabilities without needing extensive knowledge of the underlying AI technologies. For instance, a developer can use an API to integrate a natural language processing model into their application to analyze text data.How APIs Work
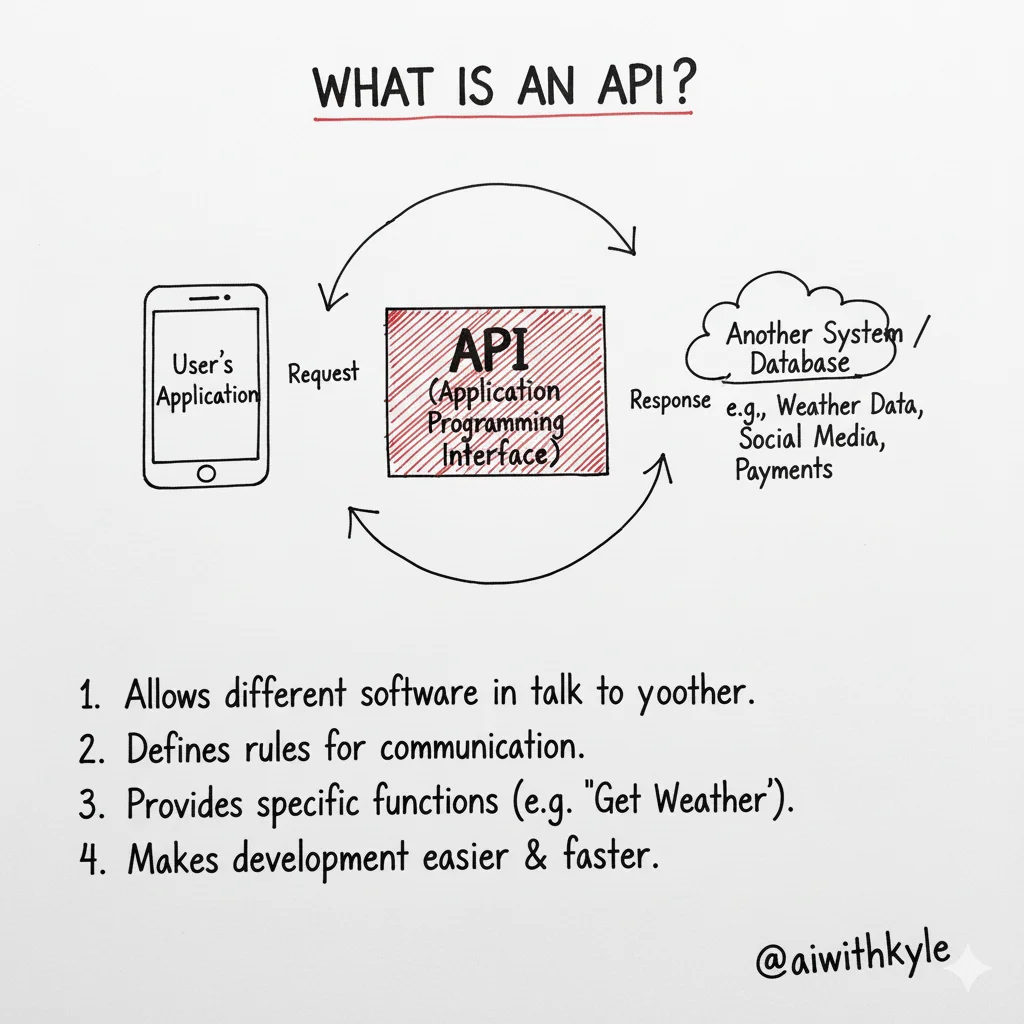
APIs operate through a series of requests and responses. When a developer wants to access an API, they send a request, typically using HTTP methods such as GET, POST, PUT, or DELETE. The API then processes this request based on the defined rules and returns a response, usually in a format like JSON or XML. This interaction allows for seamless integration and functionality across different software platforms.Current State and Future Outlook
Today, APIs are ubiquitous in software development, especially in cloud services, mobile applications, and Internet of Things (IoT) devices. As AI continues to evolve, we can expect APIs to become even more sophisticated, potentially incorporating features like real-time data processing, enhanced security protocols, and more intuitive interfaces for developers. The trend towards microservices architecture also indicates a future where APIs will be central to software design, facilitating modular and scalable applications.Real-World Examples
Google Maps API
This API allows developers to embed Google Maps on their websites or applications, enabling location-based services and navigation features.
Twitter API
Through this API, developers can access Twitter's data and functionalities, allowing them to analyze tweets, post updates, and manage Twitter accounts programmatically.
OpenAI GPT API
This API provides access to OpenAI's language models, enabling applications to generate human-like text, which is particularly useful in chatbots and content generation.
Stripe API
Stripe's API allows businesses to integrate payment processing capabilities into their websites or applications, streamlining transactions for e-commerce.
Weather API
Various weather APIs provide real-time weather data, allowing applications to deliver accurate and timely weather updates to users.
Use Cases & Applications
E-commerce Platforms
APIs are used to integrate payment gateways, inventory management systems, and shipping services, allowing seamless transactions and order fulfillment.
Social Media Integration
Applications use APIs to connect with social media platforms, enabling users to share content, post updates, and interact with their social networks.
Machine Learning Model Deployment
Developers deploy machine learning models via APIs, allowing other applications to access predictive analytics, classification, and natural language processing capabilities.
Mobile Applications
Mobile apps frequently use APIs to interact with web services, providing users with real-time data and functionalities such as user authentication and data storage.
IoT Device Communication
APIs facilitate communication between IoT devices and cloud services, enabling data collection, device management, and remote monitoring.
Video Explanation
Frequently Asked Questions
How do I use an API?
To use an API, you typically need to sign up for an API key, review the API documentation for endpoints and parameters, and make HTTP requests to interact with the API.
Are all APIs public?
No, APIs can be public, private, or partner APIs. Public APIs are available for anyone to use, while private APIs are restricted to internal use within an organization.
What is an API key?
An API key is a unique identifier used to authenticate requests made to an API, ensuring that the API can track usage and access control.
Can APIs be used for AI applications?
Yes, APIs are extensively used in AI applications to access machine learning models, natural language processing services, and other AI functionalities.
How can APIs improve software development?
APIs enable developers to leverage existing services, reduce development time, and enhance application functionality by integrating third-party tools and services.
Stories Mentioning API
Chronological timeline of all stories where this term has been discussed